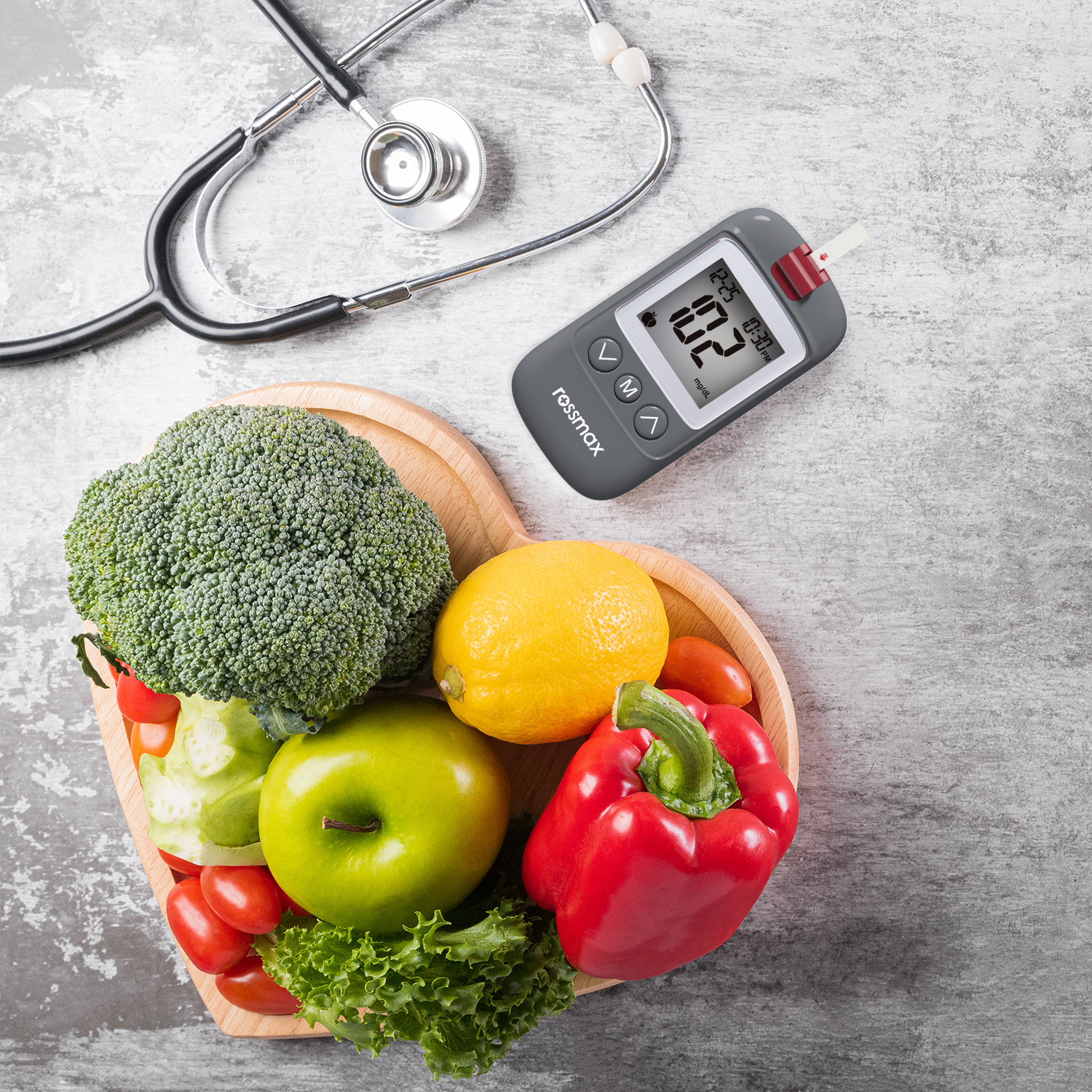
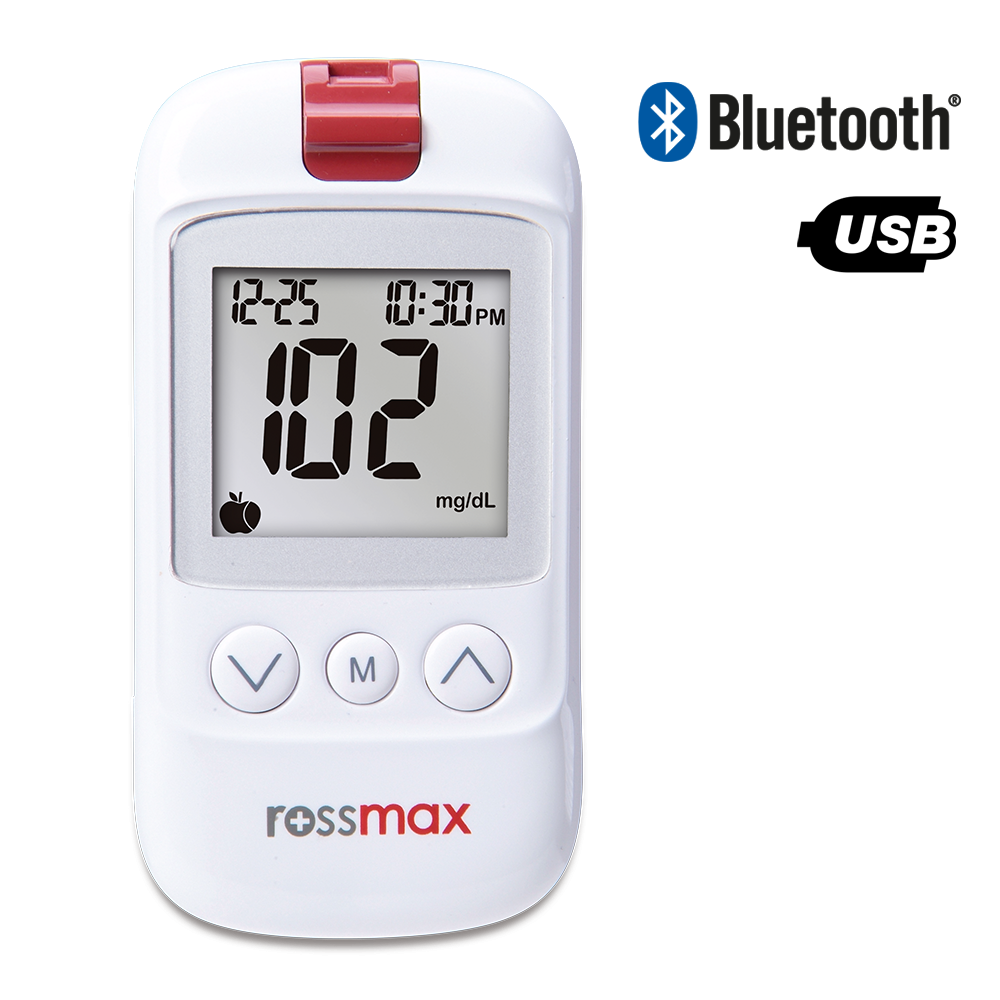
Diabetes type 2 requires ongoing maintenance, but it's also important to keep in mind that the disease will eventually progress, even if it's well-controlled. As a result, elderly diabetics' treatment plans are likely to need to be adjusted more than once in their lifetime. For diabetics, chronic high blood sugar, or hyperglycemia, can lead to a whole host of complications, including heart disease, blindness, lower limb amputations, peripheral neuropathy, and kidney damage.
The good news is that these complications can be prevented or delayed with proper diabetes management. For this reason, older adults with diabetes should eat a healthy diet, exercise regularly, and take medication as prescribed. Over time, prescription medicines, diet, and exercise recommendations will likely need to be adjusted as type 2 diabetes progresses. Having to start insulin therapy does not mean a person with type 2 diabetes has failed to manage their condition.